I’m Certified Medical Biller and Coder today we discussed about Hyperlipidemia ICD 10 Codes. In my job I’m facing many ICD-10-CM Codes, but why I’m Specially choose Hyperlipidemia ICD 10 codes. Because I remember the day I received my blood test results. My heart pounded as I scanned the page, dreading what I might find. To my dismay, there it was: ‘Hyperlipidemia.’ I’d heard the term before, but it never truly registered until it became my reality.
As I began to research this condition, I realized the importance of understanding the specific hyperlipidemia ICD 10 code associated with my diagnosis. In this blog post, I’ll share my personal journey and delve into the details of these codes. Before Jumping Hyperlipidemia ICD 10 code let’s summary what is exactly Hyperlipidemia and their Types.
What is Hyperlipidemia and their Types
Hyperlipidemia is a common health problem where there’s too much cholesterol and triglycerides in your blood. This can lead to serious heart problems.
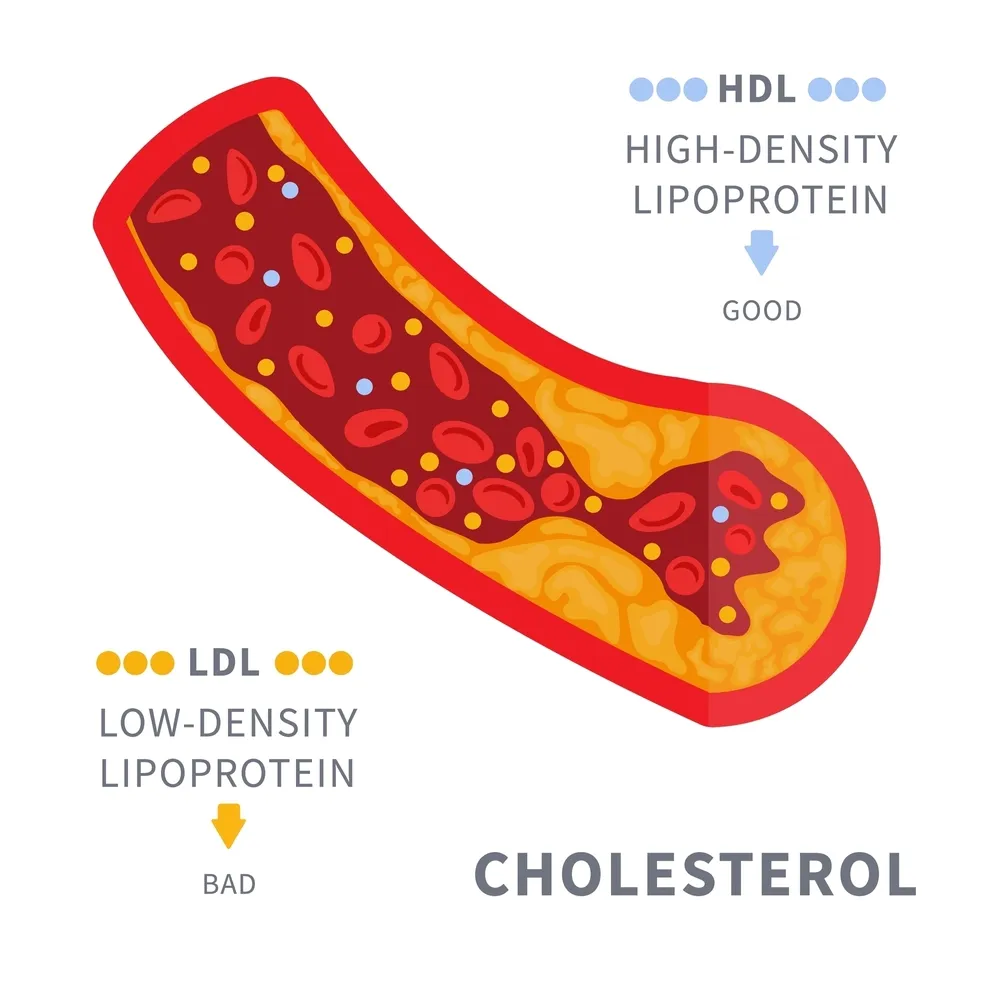
While you may already be familiar with hyperlipidemia, it’s important to understand the different types of cholesterol involved. Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, often referred to as ‘bad cholesterol,’ accumulates in the arteries, leading to plaque buildup and an increased risk of heart disease.
High-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, known as ‘good cholesterol,’ helps remove LDL cholesterol from the bloodstream.
Classifies Hyperlipidemia ICD-10 Code Under The “E”
The ICD-10 coding system plays a vital role in accurately diagnosing and classifying hyperlipidemia. Within the E category in the range E78 , specific codes are assigned to different types and subtypes of the condition, such as hypercholesterolemia and hypertriglyceridemia.
Understanding the nuances of ICD-10 codes for hyperlipidemia is crucial for healthcare providers. These codes facilitate effective communication, streamline treatment planning, and contribute to improved patient outcomes.
Hyperlipidemia vs. Dyslipidemia
Hyperlipidemia and dyslipidemia are often used interchangeably to describe conditions characterized by abnormal levels of cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood. However, there are subtle differences between these terms.
Hyperlipidemia
- Broader term that encompasses any condition involving elevated levels of lipids (cholesterol and triglycerides).
- Includes both primary (genetic) and secondary (caused by other factors) forms of hyperlipidemia.
Dyslipidemia
- More specific term that refers to an abnormal lipid profile, typically characterized by elevated LDL cholesterol, low HDL cholesterol, or elevated triglycerides.
- Often implies a combination of these abnormal lipid levels.
In essence, all cases of dyslipidemia are considered hyperlipidemia, but not all cases of hyperlipidemia are dyslipidemia.
Symptoms of Hyperlipidemia
Hyperlipidemia, often referred to as high cholesterol, is a common health condition characterized by elevated levels of cholesterol in the blood. Despite being a silent nature condition in its early stages, it can significantly increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular complications. Regular screenings and early detection are crucial for preventing these serious health issues.
Clinical Information on Mixed Hyperlipidemia
Mixed hyperlipidemia, a type of dyslipidemia, is characterized by elevated levels of both low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood. This condition significantly increases the risk of atherosclerosis and heart disease. While it may be hereditary, unhealthy lifestyle choices, such as a poor diet, lack of exercise, and excessive alcohol consumption, can also contribute to its development.
Other factors that may increase the risk of mixed hyperlipidemia include uncontrolled diabetes, hypothyroidism, kidney disease, and certain medications. Management typically involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, including a healthy diet, regular exercise, and weight management, as well as medications to help control lipid levels.
Mixed hyperlipidemia is often asymptomatic and is typically diagnosed through routine blood tests.
Synonyms for Hyperlipidemia
- Combined Hyperlipidemia
- Hypercholesterolemia with Hypertriglyceridemia
- High Cholesterol and Triglycerides
Commonly Used ICD 10 Codes for Hyperlipidemia
| Codes | Codes Description |
| E78.00 | Pure hypercholesterolemia, unspecified |
| E78.01 | Familial hypercholesterolemia |
| E78.1 | Pure Hypertriglyceridemia |
| E78.2 | Mixed hyperlipidemia |
| E78.41 | Elevated Lipoprotein(a) |
| E78.49 | Other hyperlipidemia |
| E78.5 | Hyperlipidemia, unspecified |
| E78.6 | High-density lipoprotein deficiency |
| E78.70 | Disorder of bile acid and cholesterol metabolism, unspecified |
| E78.71 | Barth syndrome |
| E78.72 | Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome |
| E78.79 | Other disorders of bile acid and cholesterol metabolism |
| E78.81 | Lipoid dermatoarthritis |
| E78.89 | Other lipoprotein metabolism disorders |
| E78.9 | Disorder of lipoprotein metabolism, unspecified |
FAQs on Hyperlipidemia ICD 10 Codes:
1. What is the ICD-10 code for hyperlipidemia?
The ICD-10 code for hyperlipidemia falls under the category E78, which covers other disorders of lipid metabolism. The specific code will depend on the type of hyperlipidemia, such as:
- E78.0: Hypercholesterolemia (high total cholesterol)
- E78.1: Hypertriglyceridemia (high triglycerides)
- E78.2: Combined hyperlipidemia (high cholesterol and triglycerides)
2. Can hyperlipidemia be coded as a secondary condition?
Yes, hyperlipidemia can be coded as a secondary condition if it is a result of another underlying medical condition. For example, if a patient has diabetes and develops hyperlipidemia as a complication, the diabetes code would be the primary diagnosis, and hyperlipidemia would be coded as a secondary condition.
3. Are there any specific guidelines or rules for coding hyperlipidemia?
There are specific guidelines and rules for coding hyperlipidemia in the ICD-10-CM manual. It’s essential to consult the official manual or seek guidance from a medical coding expert to ensure accurate coding.
4. What are the potential consequences of incorrect ICD-10 coding for hyperlipidemia?
Incorrect ICD-10 coding for hyperlipidemia can have several negative consequences, including:
- Incorrect reimbursement: If the wrong code is used, the healthcare provider may receive incorrect payment from insurance companies.
- Inaccurate data: Incorrect coding can lead to inaccurate data collection and analysis, which can impact research and public health initiatives.
- Delayed or denied treatment: If the wrong code is used, it may delay or prevent patients from receiving necessary treatment.
It’s crucial to use the correct ICD-10 code for hyperlipidemia to ensure accurate billing, data collection, and patient care.
5. How often should ICD-10 codes for hyperlipidemia be updated?
ICD-10 codes are updated annually to reflect changes in medical terminology and practices. It’s important to stay up-to-date with the latest ICD-10 codes to ensure accurate coding and billing.